Faith Brynie, Ph D
Faith Brynie holds a B.A. in Biology from West Virginia University and an M.A. and Ph.D in science curriculum and instruction from the University of Colorado. She writes books and articles on science and health topics for children, teens, and non-scientist adults. Some of her books have won awards, including two 'Best Book of the Year' citations from the American Association for the Advancement of Science.

Science Facts Written by Faith Brynie, Ph D
Why is Red-Green Colorblindness a 'Guy Thing?'
Colorblind girls and women are rare, while men who can't match their socks are relatively common. The reason is a genetic phenomenon called sex-linked inheritance. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes. ... Continue reading
What Causes Wrinkles?
Elastin and collagen are proteins in the skin's underlying layers that give it firmness and elasticity. As we age, skin begins to lose its elastin fibers. The fibers start to tangle in disorganized ... Continue reading

Splitting Hairs
Pluck a single strand of hair from your head and you've lost what scientists call the hair shaft. The shaft is made of three layers, each inside the other. The outer casing is the cuticle. Under an ... Continue reading

Types of Volcanoes
Geologists describe four types of volcanoes. Cinder cones, the simplest of volcanoes, grow as pieces of congealed lava rise from a central vent and form a funnel-shaped crater. Lava domes arise from ... Continue reading

The Placebo Effect
To test new drugs, researchers usually divide their subjects into two groups. One group receives the experimental drug. The other receives a placebo or 'sugar pill' that should have no effect on the ... Continue reading
What's So Bad About Cholesterol?
Cholesterol has a worse reputation than it deserves. This waxy lipid (a kind of fat) is essential to good health. It builds the membranes that hold cells together. It's used in making certain hormones ... Continue reading
What Is Narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is a sleep disorder than affects about 1 of every 2000 people worldwide. It usually starts in the teens or twenties, but it may begin in childhood. People who have it fall suddenly and ... Continue reading

How Did Dogs Evolve?
While the status of the dog as humankind's best and oldest friend remains unchallenged, debate rages about just how far back the friendship goes. Fossils of domesticated dogs appear in the remains of ... Continue reading

The World's Largest Clone
What's the world's largest clone? It's not a sheep, but an aspen tree...and it's a natural clone, not a human-engineered one. Nicknamed 'Pando' (Latin for 'I spread'), this 'stand' of 47,000 aspens in ... Continue reading

How Do They Grow Those Colossal Pumpkins?
Those enormous pumpkins that set records every fall are living proof that both genes and environment make living things what they are. Home gardeners out to break the 2002 record for the world's ... Continue reading

Fahrenheit 98.6
When you're well, your body temperature stays very close to 37o C. (98.6o F.), whether you're playing basketball in an overheated gym or sleeping in the stands at an ice hockey game in a snowstorm. ... Continue reading

There's No Such Thing as a Safe Suntan
Every time you step outdoors, you are bombarded by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV rays cause the number of free radicals in cells to increase. Free radicals are atoms or molecules that ... Continue reading
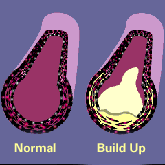
Your Friend, the Fat Cell
A healthy, adult human body contains about 35 billion fat cells. Each contains about 0.5 micrograms of fat. Stored fat is essential to good health. Fat is the body's principal energy reserve. It is ... Continue reading

What Gives Hair Its Color?
Put a single hair under a microscope, and you'll see granules of black, brown, yellow, or red pigment. What you are seeing are tiny particles of melanin, the same pigment that gives skin its color. ... Continue reading
Why Is Blood Pressure Two Numbers?
Blood pressure might better be called heart pressure, for the heart's pumping action creates it. To measure blood pressure, health workers determine how hard the blood is pushing at two different ... Continue reading

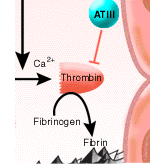
How Blood Clots
Scabby knees and bruised shins are as much a part of growing up as climbing trees. Minor injuries from paper cuts to skinned elbows are nothing to worry about for most people, because the blood's ... Continue reading
Exercising In Space
What did astronaut Shannon Lucid like least about her six months on Space Station Mir? The daily exercise. 'It was just downright hard,' she wrote in Scientific American (May 1998). 'I had to put on a ... Continue reading

What Is a Bruise?
A bruise is a deposit of blood under the skin. It flows from tiny capillaries that break when you bump your shin on the furniture or take the batter's pop fly in the eye. The injury starts out looking ... Continue reading

When Motherhood Means More than One
These days, twins, triplets, and other multiple births are becoming more common, but how do they happen? Fraternal twins (or triplets, quadruplets, or more) develop when two or more eggs are ... Continue reading

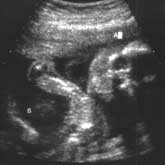
Ultrasound In Medicine
In medical testing, ultrasound equipment is used to produce a sonogram, or a picture of organs inside the body. Ultrasound scanners do not use X-rays. They use waves of such high frequency that they ... Continue reading
Hypotension
Bend to select a book from the lowest shelf, then rise quickly. Chances are, you'll feel a little lightheaded for a few seconds. The reason is a drop of blood pressure caused by the change in ... Continue reading

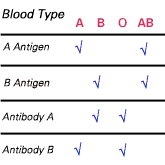
What Are Blood Types, and Why Are They Important?
If your medical report reads A, Rh+, M, s, P1, Lua, K+, Kp(a-b+), Le(a-b+). Fy(a+), Jk(a+b+), don't run for a foreign language dictionary. The letters aren't Greek. They are simply the names given to ... Continue reading

Mad Cow Disease
In 1986, the first case of 'mad cow' disease or bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) was found in cattle in Great Britain. Irritable personalities, fearful behavior, and a staggering gait preceded ... Continue reading

Serendipity In Science
Most scientists accept the notion that serendipity plays a major role in their work. Too many discoveries have been, after all, the result of 'lucky accidents.' In the 16th century, for example, ... Continue reading

Sex and the Sea Slug
The sea slug, Aplysia. Now there's an expert on sex. Equipped with both male and female sex organs, this shell-less, subtidal mollusk lives alone most of the year. It loses its self-sufficiency, ... Continue reading

Fahrenheit 100 and Rising
When you are well, your body temperature varies only a little around 37o C. (98.6o F.), whether you're sweating in a steam room or hiking in the Yukon. The hypothalamus in the brain controls body ... Continue reading

When and Why is Blood Typing Done?
Fans of the popular television show ER know how important blood type is in an emergency. 'Start the O-neg,' shouts Doctor Green, and the team swings into action. Green calls for type O, Rh-negative ... Continue reading
It's Hay Fever Season!
If spring's flying pollen is making you sneeze, you are not alone. Some 40 to 50 million people in the United States complain of respiratory allergies, and experts estimate that three to four million ... Continue reading
A Sweaty Subject
When human body temperature rises, tiny muscles around the sweat glands in the skin contract, squeezing perspiration - better known as sweat - out through the pores. Sweat is about 99 percent water. ... Continue reading

Is Heartburn a Heart Burn?
Heartburn is a bad name for a complaint that has nothing to do with the heart. TV ads call it acid indigestion. It's a burning sensation that begins under the breastbone and moves up into the throat. ... Continue reading