What Are Stem Cells?
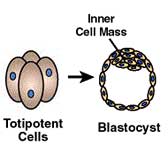 When an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell, it quickly becomes a single cell from which all cells of the body-to-be will be created. This 'mother of all cells' is what biologists call a totipotent stem cell, meaning that it has unlimited creative power. Within a few days, the totipotent stem cell begins a process of division into a hollow sphere (a blastocyst) containing a slightly more specialized level of stem cells. These stem cells are known as pluripotent, meaning that they are capable of generating most, but not all, the cells of the developing organism - all the cells except for the placenta and other supporting tissues a developing fetus would need to survive in the uterus.
When an egg is fertilized by a sperm cell, it quickly becomes a single cell from which all cells of the body-to-be will be created. This 'mother of all cells' is what biologists call a totipotent stem cell, meaning that it has unlimited creative power. Within a few days, the totipotent stem cell begins a process of division into a hollow sphere (a blastocyst) containing a slightly more specialized level of stem cells. These stem cells are known as pluripotent, meaning that they are capable of generating most, but not all, the cells of the developing organism - all the cells except for the placenta and other supporting tissues a developing fetus would need to survive in the uterus.
From the pluripotent stem cells, further levels of increasingly specialized cells are created, leading ultimately to each individual cell of the body. Some types of stem cell continue to exist in the body after birth - indeed, throughout the life of the organism. Blood stem cells, for example, generate new red blood cells, white blood cells, and blood platelets ad infinitum. They cannot generate all the types of cell in the body, so they are not totipotent or pluripotent, but they are still multipotent, capable of generating a number of different kinds of cells of a general type, such as blood or skin.
About the Author
David Gamon, PhD
 Dr. David Gamon, one of the original writers at ScienceIQ, studied cognitive science at U.C. Berkeley, where he received his Ph.D. in Linguistics in 1997. He is the author of many popular books about the human brain, including Building Mental Muscle, Use It Or Lose It!, and Brains That Work a Little Bit Differently. His current projects include books about gender differences in the brain, the brain’s construction of sensory reality, and psychopathy.
Dr. David Gamon, one of the original writers at ScienceIQ, studied cognitive science at U.C. Berkeley, where he received his Ph.D. in Linguistics in 1997. He is the author of many popular books about the human brain, including Building Mental Muscle, Use It Or Lose It!, and Brains That Work a Little Bit Differently. His current projects include books about gender differences in the brain, the brain’s construction of sensory reality, and psychopathy.


