Robin's Egg Blue
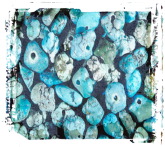 Turquoise, the robin's egg blue gemstone worn by Pharaohs and Aztec Kings, is probably one of the oldest gemstones known. Yet, only its prized blue color, a color so distinctive that its name is used to describe any color that resembles it, results in its being used as a gemstone. Turquoise has been, since about 200 B.C., extensively used by both southwestern U.S. Native Americans and by many of the Indian tribes in Mexico. The Native American Jewelry or 'Indian style' jewelry with turquoise mounted in or with silver is relatively new. Some believe this style of Jewelry was unknown prior to about 1880, when a white trader persuaded a Navajo craftsman to make turquoise and silver jewelry using coin silver. Prior to this time, the Native Americans had made solid turquoise beads, carvings, and inlaid mosaics. Recently, turquoise has found wide acceptance among people of all walks of life and from many different ethnic groups.
Turquoise, the robin's egg blue gemstone worn by Pharaohs and Aztec Kings, is probably one of the oldest gemstones known. Yet, only its prized blue color, a color so distinctive that its name is used to describe any color that resembles it, results in its being used as a gemstone. Turquoise has been, since about 200 B.C., extensively used by both southwestern U.S. Native Americans and by many of the Indian tribes in Mexico. The Native American Jewelry or 'Indian style' jewelry with turquoise mounted in or with silver is relatively new. Some believe this style of Jewelry was unknown prior to about 1880, when a white trader persuaded a Navajo craftsman to make turquoise and silver jewelry using coin silver. Prior to this time, the Native Americans had made solid turquoise beads, carvings, and inlaid mosaics. Recently, turquoise has found wide acceptance among people of all walks of life and from many different ethnic groups.
For thousands of years the finest intense blue turquoise in the world was found in Persia, and the term 'Persian Turquoise' became synonymous with the finest quality. This changed during the late 1800's and early 1900's when modern miners discovered or rediscovered significant deposits of high-quality turquoise in the western and southwestern United States. Material from many of these deposits was just as fine as the finest 'Persian.' Today, the term 'Persian Turquoise' is more often a definition of quality than a statement of origin, and the majority of the world's finest-quality turquoise comes from the United States, the largest producer of turquoise.
The increased acceptance of turquoise resulted in higher prices, some of the most desirable materials going for as much as $2,200 per kg. The increased demand could not be met through production of acceptable mine run materials. Therefore, an industry emerged--the business of turquoise stabilization, reconstitution, and the manufacture of synthetic and simulated turquoise. In most instances, the stabilization and reconstitution of turquoise involve the use of earthy or highly porous types of turquoise which are pressure-impregnated with hot acrylic resins. The resins improve the color, hardness, and durability of the material to a point that inexpensive porous, poorly colored, or nearly colorless materials become suitable for use in jewelry. As long as the materials are represented as treated, stabilized, or reconstituted, the marketplace can accept or reject the materials based on decisions that are purely business or economic.
Fact Credit
USGS General


