USGS General

Science Facts Written by USGS General
Water In The Ground
Some water underlies the Earth's surface almost everywhere, beneath hills, mountains, plains, and deserts. It is not always accessible, or fresh enough for use without treatment, and it's sometimes ... Continue reading

The Richter Magnitude Scale
Seismic waves are the vibrations from earthquakes that travel through the Earth; they are recorded on instruments called seismographs. Seismographs record a zig-zag trace that shows the varying ... Continue reading

Geology Played Key Role in the End of the Civil War
Depending on your perspective, Mississippi geology was either an aiding ally or formidable foe as Union troops tried to take control of the Mighty Mississippi. It was May, 141 years ago, and Major ... Continue reading

The San Andreas Fault
Scientists have learned that the Earth's crust is fractured into a series of 'plates' that have been moving very slowly over the Earth's surface for millions of years. Two of these moving plates meet ... Continue reading

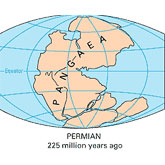
Pangea
From about 280-230 million years ago, (Late Paleozoic Era until the Late Triassic) the continent we now know as North America was continuous with Africa, South America, and Europe. Pangea first began ... Continue reading
Plate Tectonics
In geologic terms, a plate is a large, rigid slab of solid rock. The word tectonics comes from the Greek root 'to build.' Putting these two words together, we get the term plate tectonics, which ... Continue reading
What Elements Are Required By Animals And Plants For Survival?
An understanding of our fragile environment can begin with a recognition of the importance of certain elements, commonly called 'mineral substances' (such as iron and zinc), in the lives of humans and ... Continue reading

The Hydrology of Drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions that results in water-related problems. Precipitation (rain or snow) falls in uneven patterns across the country. The amount of precipitation at a ... Continue reading

The Mineral Chalcedony
Chalcedony is a catch all term that includes many well known varieties of cryptocrystalline quartz gemstones. They are found in all 50 States, in many colors and color combinations, and in ... Continue reading
All That Glitters
Gold is called a 'noble' metal because it does not oxidize under ordinary conditions. Its chemical symbol Au is derived from the Latin word 'aurum.' In pure form gold has a metallic luster and is sun ... Continue reading

Why Are Zebra Mussels Successful As Invaders?
The zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) is a small, non-native mussel originally found in Russia. In 1988, this animal was transported to North America in the ballast water of a transatlantic ... Continue reading

Predicting Floods
Several types of data can be collected to assist hydrologists predict when and where floods might occur. The first and most important is monitoring the amount of rainfall occurring on a realtime ... Continue reading

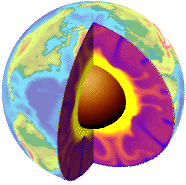
Under The Crust
Three centuries ago, the English scientist Isaac Newton calculated, from his studies of planets and the force of gravity, that the average density of the Earth is twice that of surface rocks and ... Continue reading
What is Volcanic Ash?
Small jagged pieces of rocks, minerals, and volcanic glass the size of sand and silt (less than 1/12 inch or 2 millimeters in diameter) erupted by a volcano are called volcanic ash. Very small ash ... Continue reading

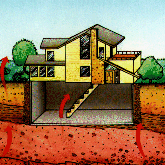
Radioactive Radon
Radon is a gas produced by the radioactive decay of the element radium. Radioactive decay is a natural, spontaneous process in which an atom of one element decays or breaks down to form another ... Continue reading
Salty Remnants At Death Valley's Badwater
Beneath the dark shadows of the Black Mountains, a great, extraordinarily flat expanse of shimmering white spreads out before you. You are at Badwater, at -282 feet it is the lowest spot in the ... Continue reading

Was That The Big One? Depends On How You Measured It.
The severity of an earthquake can be expressed in terms of both intensity and magnitude. However, the two terms are quite different, and they are often confused. Intensity is based on the observed ... Continue reading

Submarine Volcanoes
Submarine volcanoes and volcanic vents are common features on certain zones of the ocean floor. Some are active at the present time and, in shallow water, disclose their presence by blasting steam and ... Continue reading

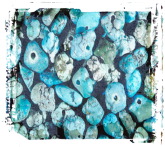
Robin's Egg Blue
Turquoise, the robin's egg blue gemstone worn by Pharaohs and Aztec Kings, is probably one of the oldest gemstones known. Yet, only its prized blue color, a color so distinctive that its name is used ... Continue reading
Earthquake Weather?
In the 4th Century B.C., Aristotle proposed that earthquakes were caused by winds trapped in subterranean caves. Small tremors were thought to have been caused by air pushing on the cavern roofs, and ... Continue reading

A Voggy Day On The Big Island
On the morning of February 8, 2000, Harry Kim, Director of Hawai`i County Civil Defense, asked radio stations on the Island of Hawai`i to broadcast a special message concerning the thick, acrid haze ... Continue reading

Pointing North
The needle of a compass is a small magnet, one that is allowed to pivot in the horizontal plane. The needle experiences a torque from the ambient magnetic field of the Earth. The reaction to this ... Continue reading

