NIH NCBI

Science Facts Written by NIH NCBI
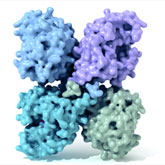
Proteins Function Through Their Conformation
To produce proteins, cellular structures called ribosomes join together long chains of subunits. A set of 20 different subunits, called amino acids, can be arranged in any order to form a polypeptide ... Continue reading
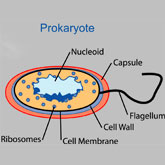
Prokaryotic Organisms
It appears that life arose on earth about 4 billion years ago. The simplest of cells, and the first types of cells to evolve, were prokaryotic cells--organisms that lack a nuclear membrane, the ... Continue reading
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the field of science in which biology, computer science, and information technology merge to form a single discipline. The ultimate goal of the field is to enable the discovery of ... Continue reading
Classifying Organisms
Have you ever noticed that when you see an insect or a bird, there is real satisfaction in giving it a name, and an uncomfortable uncertainty when you can't? Along these same lines, consider the ... Continue reading

Genome Mapping: A Guide To The Genetic Highway We Call The Human Genome
Imagine you're in a car driving down the highway to visit an old friend who has just moved to Los Angeles. Your favorite tunes are playing on the radio, and you haven't a care in the world. You stop ... Continue reading

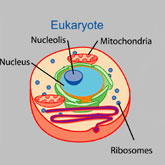
Eukaryotic Organisms
Eukaryotes include fungi, animals, and plants as well as some unicellular organisms. Eukaryotic cells are about 10 times the size of a prokaryote and can be as much as 1000 times greater in volume. ... Continue reading
Microarrays: Chipping Away At The Mysteries Of Science And Medicine
With only a few exceptions, every cell of the body contains a full set of chromosomes and identical genes. Only a fraction of these genes are turned on, however, and it is the subset that is ... Continue reading

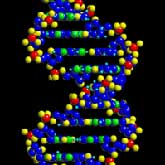
Proteins In General
Proteins form our bodies and help direct its many systems. Proteins are fundamental components of all living cells. They exhibit an enormous amount of chemical and structural diversity, enabling them ... Continue reading